前回の第34回
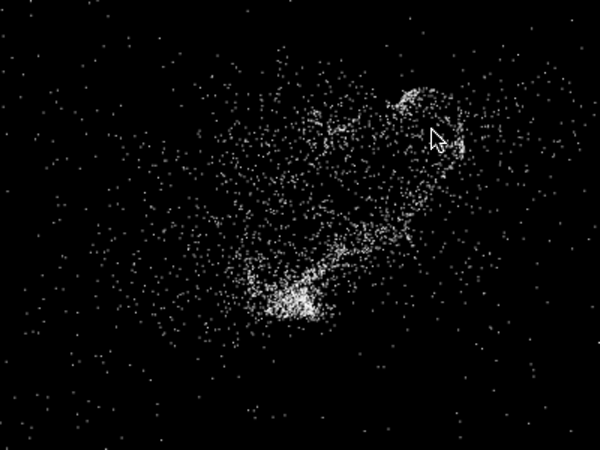
たくさんのパーティクルをステージのランダムな位置に置く
前回の第34回コード6に手を加えよう。パーティクルのクラス
// var particle;
var particles = new Array();
var numParticles = 3000;
function initialize() {
// createParticle();
createParticles(numParticles);
}
// function createParticle() {
function createParticles(amount) {
for (var i = 0; i < amount; i++) {
var _x = Math.random() * stageWidth;
var _y = Math.random() * stageHeight;
// particle = new Particle(stageWidth / 2, stageHeight / 2, stageWidth, stageHeight);
var particle = new Particle(_x, _y, stageWidth, stageHeight);
particles.push(particle);
stage.addChild(particle);
}
}呼び出された関数
// createjs.Ticker.addEventListener("tick", updateAnimation);
すべてのパーティクルを弾けるように動かす
つぎは、
function updateAnimation(eventObject) {
var count = particles.length;
// particle.accelerateTo(mouseX, mouseY);
for (var i = 0; i < count; i++) {
var particle = particles[i];
particle.accelerateTo(mouseX, mouseY);
}
}クラス

var stage;
var stageWidth;
var stageHeight;
var mousePoint = new createjs.Point();
var particles = [];
var numParticles = 3000;
function initialize() {
var canvasElement = document.getElementById("myCanvas");
stageWidth = canvasElement.width;
stageHeight = canvasElement.height;
stage = new createjs.Stage(canvasElement);
mousePoint.x = stageWidth / 2;
mousePoint.y = stageHeight / 2;
createParticles(numParticles);
stage.update();
stage.addEventListener("stagemousemove", recordMousePoint);
createjs.Ticker.timingMode = createjs.Ticker.RAF;
createjs.Ticker.addEventListener("tick", updateAnimation);
}
function recordMousePoint(eventObject) {
mousePoint.x = eventObject.stageX;
mousePoint.y = eventObject.stageY;
}
function updateAnimation(eventObject) {
var count = particles.length;
var mouseX = mousePoint.x;
var mouseY = mousePoint.y;
for (var i = 0; i < count; i++) {
var particle = particles[i];
particle.accelerateTo(mouseX, mouseY);
}
stage.update();
}
function createParticles(amount) {
for (var i = 0; i < amount; i++) {
var _x = Math.random() * stageWidth;
var _y = Math.random() * stageHeight;
var particle = new Particle(_x, _y, stageWidth, stageHeight);
particles[i] = particle;
stage.addChild(particle);
}
}function Particle(x, y, right, bottom) {
this.initialize();
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.right = right;
this.bottom = bottom;
this.velocityX = 0;
this.velocityY = 0;
this.friction = 0.95;
this.radius = 0.5;
this.drawParticle();
}
Particle.prototype = new createjs.Shape();
Particle.prototype.drawParticle = function () {
var size = this.radius * 2;
this.graphics.beginFill("white")
.drawRect(-this.radius, -this.radius, size, size);
};
Particle.prototype.accelerateTo = function (targetX, targetY) {
var _x = this.x;
var _y = this.y;
var _velocityX = this.velocityX;
var _velocityY = this.velocityY;
var differenceX = targetX - _x;
var differenceY = targetY - _y;
var square = differenceX * differenceX + differenceY * differenceY;
var ratio;
if (square > 0) {
ratio = 50 / square;
} else {
ratio = 0;
}
var accelerationX = differenceX * ratio;
var accelerationY = differenceY * ratio;
_velocityX += accelerationX;
_velocityY += accelerationY;
_velocityX *= this.friction;
_velocityY *= this.friction;
_x += _velocityX;
_y += _velocityY;
if (_x < 0) {
_x += this.right;
} else if (_x > this.right) {
_x -= this.right;
}
if (_y < 0) {
_y += this.bottom;
} else if (_y > this.bottom) {
_y -= this.bottom;
}
this.x = _x;
this.y = _y;
this.velocityX = _velocityX;
this.velocityY = _velocityY;
};配列の扱いを最適化する
前掲コード1は、
// var particles = new Array();
var particles = [];
function createParticles(amount) {
for (var i = 0; i < amount; i++) {
var particle = new Particle(_x, _y, stageWidth, stageHeight);
// particles.push(particle);
particles[i] = particle;
}
}第1に、
配列の扱いは、
まず、
| コンストラクタ呼出し | 引数の意味 | つくられる配列 |
|---|---|---|
| new Array() | エレメント | [] |
| new Array(3) | 長さ | [undefined, undefined, undefined] |
| new Array(0, 1, 2) | エレメント | [0, 1, 2] |
| new Array("a") | エレメント | ["a"] |
このようにArray()コンストラクタは、

つぎに、

結局、
配列[配列.length] = エレメントでは、
しかも、
配列はたくさんのエレメントをまとめて、



