はじめに
今回は、
平面走査法と水平方向
前回は、
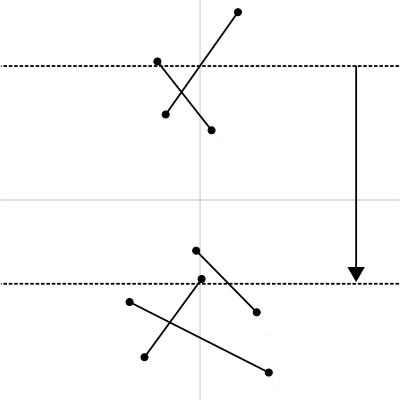
実は、
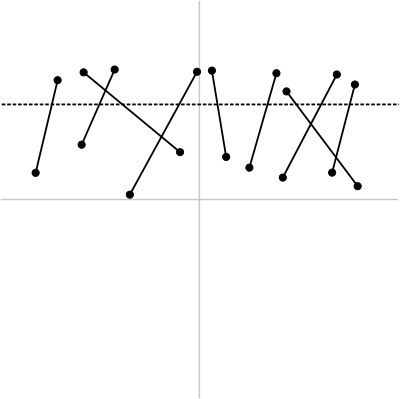
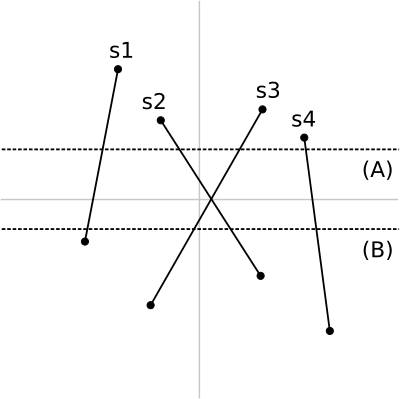
この状況を改善するには、
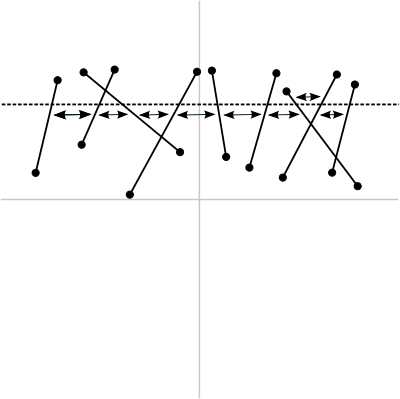
平面走査法のデータ構造
以上が、
なお、
イベント
走査線は上から下まで動かすと先に述べました。しかし、
イベント点になるのは、
イベントオブジェクトは、
イベントキュー
イベントキューは、
ステータス
ステータスは、
順序付き集合:TreeSetクラス
イベントキューとステータスのところで、
- ・
add(element) - 集合にelementを追加します。
- ・
remove(element) - 集合からelementを削除します。
- ・
pollFirst() - Java 6以降 - 先頭
(最小) の要素を取得し、 その要素を集合から削除します。集合が空の場合はnullを返します。 - ・
lower(element) - Java 6以降 - elementよりも小さい要素のうち、
最大のものを返します。elementよりも小さい要素が存在しない場合はnullを返します。 - ・
higher(element) - Java 6以降 - elementよりも大きい要素のうち、
最小のものを返します。elementよりも大きい要素が存在しない場合はnullを返します。
TreeSetクラスの非常に重要な特徴は、
イベントクラス
それでは、
public class Event implements Comparable<Event> {
public enum Type { // イベントの種類
SEGMENT_START, // 線分の始点
SEGMENT_END, // 線分の終点
INTERSECTION // 線分同士の交差
}
public Type type;
public double x;
public double y;
// 点に関連する線分1
public LineSegment segment1;
// 点に関連する線分2(type = INTERSECTIONのときのみ使用)
public LineSegment segment2;
public Event(Type type, double x, double y, LineSegment segment1,
LineSegment segment2) {
this.type = type;
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.segment1 = segment1;
this.segment2 = segment2;
}
// Comparable<Event>>の実装
public int compareTo(Event e) {
int c = Double.compare(y, e.y); // イベント点のy座標を比較
if (c == 0) { // y座標が等しい場合はx座標を比較
c = Double.compare(x, e.x);
}
return c;
}
}走査線ベースの線分コンパレータ
次に、
SweepLineBasedComparatorクラスを作成するときに注意が必要なのは、
以上のルールを実装したものが、
public class SweepLineBasedComparator implements Comparator<LineSegment> {
private Line sweepLine;
private Line belowLine;
public SweepLineBasedComparator() {
setY(0);
}
// 走査線のy座標を更新
public void setY(double y) {
// 走査線を更新
sweepLine = Line.fromPoints(0, y, 1, y);
// 走査線の少し下を通る線を作成
belowLine = Line.fromPoints(0, y + 0.1, 1, y + 0.1);
}
// Comparator<LineSegment>の実装
public int compare(LineSegment s1, LineSegment s2) {
int c = compareByLine(s1, s2, sweepLine);
if (c == 0) { // 走査線上の交点が等しい場合は、走査線の少し下の位置で比較
c = compareByLine(s1, s2, belowLine);
}
return c;
}
// s1とs2を、lineとの交点のx座標にもとづいて比較
private int compareByLine(LineSegment s1, LineSegment s2, Line line) {
Point2D p1 = s1.toLine().getIntersectionPoint(line);
Point2D p2 = s2.toLine().getIntersectionPoint(line);
// 交点がnull(線分とlineが平行)の場合は線分の1端点を比較値に採用
double x1 = p1 != null ? p1.getX() : s1.x1;
double x2 = p2 != null ? p2.getX() : s2.x1;
return Double.compare(x1, x2);
}
}上のコードで、
まとめと次回予告
今回は、
今回作成したプログラムのソースコードがダウンロードできます。
- 第4回ソースコードファイル
(gihyo-geometry-part4. zip/ Zip圧縮/約57KB)
次回は、



